What is Hepatitis B Virus (HBV)?
- HBV is a virus infection of the liver.
- HBV is transmitted through the exchange of bodily fluids, the surface of needles, or to newborn children.
- The World Health Organization estimates that ~2 billion people have contracted HBV.
- Approximately 300 million people are currently living with chronic HBV infection.
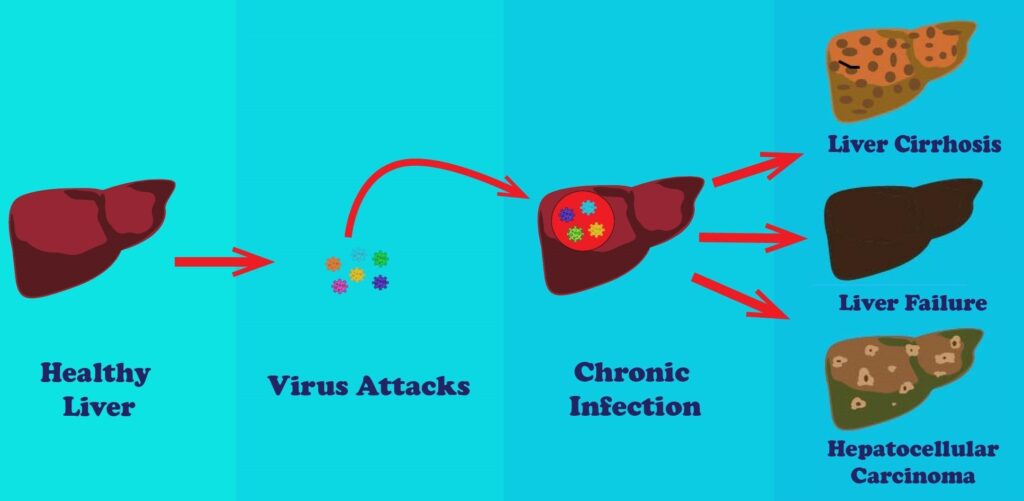
- Chronic HBV infection is a leading cause of liver cirrhosis (fibrosis) and hepatocellular carcinoma (liver cancer).
- HBV is responsible for nearly 1 million deaths each year.
- Preventative HBV vaccines are available and provide protection when administered early in life.
- Chronic HBV infection remains a high priority unmet medical need.
- Approved drugs include nucleoside analogs and interferon alpha (an immunotherapy). These are required lifelong.
- There is no cure for chronic HBV infection.
Complications of Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection
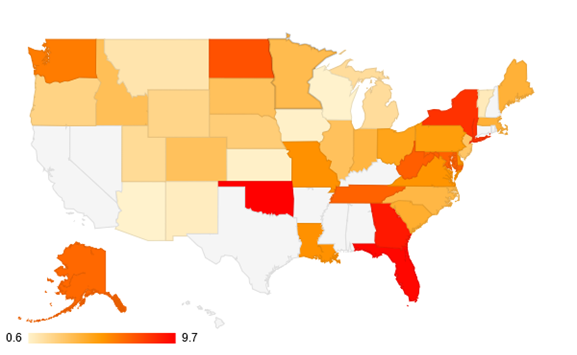
Chronic HBV Prevalence in the United States
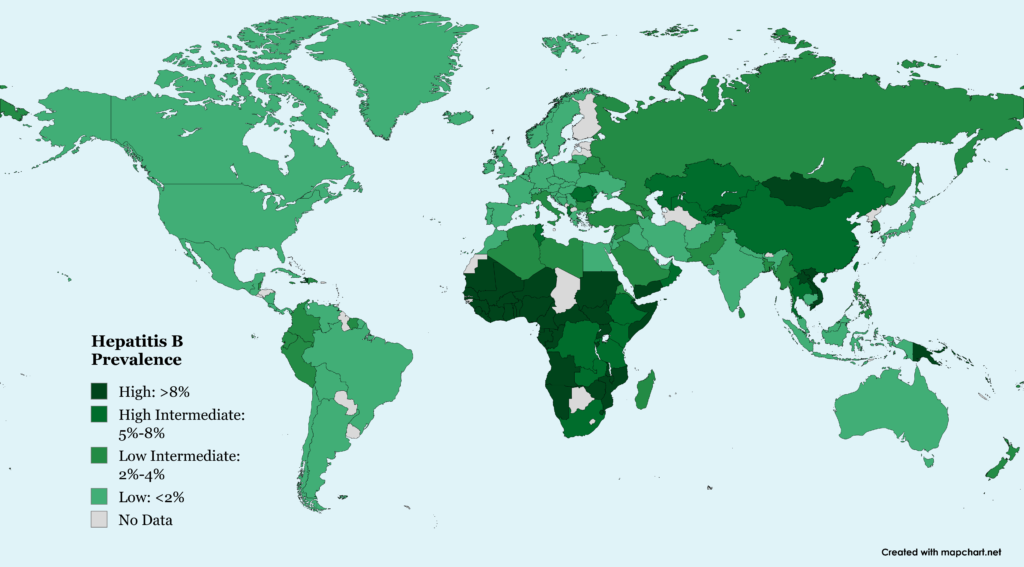
Worldwide Chronic HBV Infection Prevalence Rates
Approved Drugs to Treat HBV Infection (Not Curative)
| Marketed Name | Drug | Class |
|---|---|---|
| Viread® | Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate | Nucleoside Analog |
| Vemlidy® | Tenofovir Alafenamide Fumarate | Nucleoside Analog |
| Baraclude® | Entecavir | Nucleoside Analog |
| Tyzeka® | Telbivudine (discontinued) | Nucleoside Analog |
| Hepsera® | Adefovir Dipivoxil | Nucleoside Analog |
| Epivir HBV® | Lamivudine | Nucleoside Analog |
| Pegasys® | Pegylated Interferon | Immunomodulator |
| Intron A® | Interferon Alpha | Immunomodulator |
More Information about HBV can be found on the NIH website and from the
World Health Organization Global Hepatitis Report 2024.